Why the U.S. Seeks to Hem in Russia, China and Iran
America’s three principal adversaries signify the shape of the world to come: a post-Western world of coexistence. But neoliberal and neocon ideology is unable to to accept global pluralism and multipolarity, argues Patrick Lawrence.
The Trump administration has brought U.S. foreign policy to the brink of crisis, if it has not already tipped into one. There is little room to argue otherwise. In Asia, Europe, and the Middle East, and in Washington’s ever-fraught relations with Russia, U.S. strategy, as reviewed in my previous column, amounts to little more than spoiling the efforts of others to negotiate peaceful solutions to war and dangerous standoffs in the interests of an orderly world.
The bitter reality is that U.S. foreign policy has no definable objective other than blocking the initiatives of others because they stand in the way of the further expansion of U.S. global interests. This impoverished strategy reflects Washington’s refusal to accept the passing of its relatively brief post–Cold War moment of unipolar power.
There is an error all too common in American public opinion. Personalizing Washington’s regression into the role of spoiler by assigning all blame to one man, now Donald Trump, deprives one of deeper understanding. This mistake was made during the steady attack on civil liberties after the Sept. 11 tragedies and then during the 2003 invasion of Iraq: namely that it was all George W. Bush’s fault. It was not so simple then and is not now. The crisis of U.S. foreign policy—a series of radical missteps—are systemic. Having little to do with personalities, they pass from one administration to the next with little variance other than at the margins.
Let us bring some history to this question of America as spoiler. What is the origin of this undignified and isolating approach to global affairs?
It began with that hubristic triumphalism so evident in the decade after the Cold War’s end. What ensued had various names.
There was the “end of history” thesis. American liberalism was humanity’s highest achievement, and nothing would supersede it.
There was also the “Washington consensus.” The world was in agreement that free-market capitalism and unfettered financial markets would see the entire planet to prosperity. The consensus never extended far beyond the Potomac, but this sort of detail mattered little at the time.
The neoliberal economic crusade accompanied by neoconservative politics had its intellectual ballast, and off went its true-believing warriors around the world.

Happier days with Russia. (Eric Draper)
Failures ensued. Iraq post–2003 is among the more obvious. Nobody ever planted democracy or built free markets in Baghdad. Then came the “color revolutions,” which resulted in the destabilization of large swathes of the former Soviet Union’s borderlands. The 2008 financial crash followed.
I was in Hong Kong at the time and recall thinking, “This is not just Lehman Brothers. An economic model is headed into Chapter 11.” One would have thought a fundamental rethink in Washington might have followed these events. There has never been one.
The orthodoxy today remains what it was when it formed in the 1990s: The neoliberal crusade must proceed. Our market-driven, “rules-based” order is still advanced as the only way out of our planet’s impasses.
A Strategic and Military Turn
Midway through the first Obama administration, a crucial turn began. What had been an assertion of financial and economic power, albeit coercive in many instances, particularly with the invasions of Iraq and Afghanistan, took on further strategic and military dimensions. The NATO bombing campaign in Libya, ostensibly a humanitarian mission, became a regime-change operation—despite Washington’s promises otherwise. Obama’s “pivot to Asia” turned out to be a neo-containment policy toward China. The “reset” with Russia, declared after Obama appointed Hillary Clinton secretary of state, flopped and turned into the virulent animosity we now live with daily. The U.S.-cultivated coup in Kiev in 2014 was a major declaration of drastic turn in policy towards Moscow. So was the decision, taken in 2012 at the latest, to back the radical jihadists who were turning civil unrest in Syria into a campaign to topple the Assad government in favor of another Islamist regime.
Spoilage as a poor excuse for a foreign policy had made its first appearances.
I count 2013 to 2015 as key years. At the start of this period, China began developing what it now calls its Belt and Road Initiative—its hugely ambitious plan to stitch together the Eurasian landmass, Shanghai to Lisbon. Moscow favored this undertaking, not least because of the key role Russia had to play and because it fit well with President Vladimir Putin’s Eurasian Economic Union (EAEU), launched in 2014.
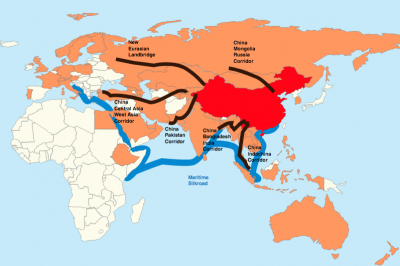
Belt and Road Initiative. (Lommes / CC BY-SA 4.0)
In 2015, the last of the three years I just noted, Russia intervened militarily and diplomatically in the Syria conflict, in part to protect its southwest from Islamist extremism and in part to pull the Middle East back from the near-anarchy then threatening it as well as Russia and the West.
Meanwhile, Washington had cast China as an adversary and committed itself—as it apparently remains—to regime change in Syria. Three months prior to the treaty that established the EAEU, the Americans helped turn another case of civil unrest into a regime change—this time backing not jihadists in Syria but the crypto-Nazi militias in Ukraine on which the government now in power still depends.
That is how we got the U.S.-as-spoiler foreign policy we now have.
If there is a president to blame—and again, I see little point in this line of argument—it would have to be Barack Obama. To a certain extent, Obama was a creature of those around him, as he acknowledged in his interview with Jeffrey Goldberg in The Atlantic toward the end of his second term. From that “Anonymous” opinion piece published in The New York Times on Sept. 5, we know Trump is too, to a greater extent than Obama may have feared in his worst moments.
The crucial question is why. Why do U.S. policy cliques find themselves bereft of imaginative thinking in the face of an evolving world order? Why has there been not a single original policy initiative since the years I single out, with the exception of the now-abandoned 2015 accord governing Iran’s nuclear programs? “Right now, our job is to create quagmires until we get what we want,” an administration official told The Washington Post’s David Ignatius in August.
Can you think of a blunter confession of intellectual bankruptcy? I can’t.
Global ‘Equals’ Like Us?
There is a longstanding explanation for this paralysis. Seven decades of global hegemony, the Cold War notwithstanding, left the State Department with little to think about other than the simplicities of East-West tension. Those planning and executing American diplomacy lost all facility for imaginative thinking because there was no need of it. This holds true, in my view, but there is more to our specific moment than mere sclerosis within the policy cliques.
As I have argued numerous times elsewhere, parity between East and West is a 21st century imperative. From Woodrow Wilson to the post-World War II settlement, an equality among all nations was in theory what the U.S. considered essential to global order.
Now that this is upon us, however, Washington cannot accept it. It did not count on non-Western nations achieving a measure of prosperity and influence until they were “just like us,” as the once famous phrase had it. And it has not turned out that way.

Can’t we all just get along? (Carlos3653 / Wikimedia)
Think of Russia, China, and Iran, the three nations now designated America’s principal adversaries. Each one is fated to become (if it is not already) a world or regional power and a key to stability—Russia and China on a global scale, Iran in the Middle East. But each stands resolutely—and this is not to say with hostile intent—outside the Western-led order. They have different histories, traditions, cultures, and political cultures. And they are determined to preserve them.
They signify the shape of the world to come—a post-Western world in which the Atlantic alliance must coexist with rising powers outside its orbit. Together, then, they signify precisely what the U.S. cannot countenance. And if there is one attribute of neoliberal and neoconservative ideology that stands out among all others, it is its complete inability to accept difference or deviation if it threatens its interests.
This is the logic of spoilage as a substitute for foreign policy. Among its many consequences are countless lost opportunities for global stability.